
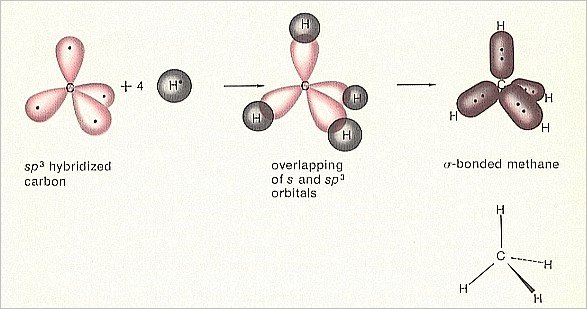
In conclusion, pi bonds are essential to covalent bonding, giving compounds with double and triple bonds their distinct characteristics. They participate in processes where pi bonds are broken to create new sigma bonds, such as addition reactions. Pi bonds are important in the chemistry of organic substances and are necessary for the stability and characteristics of molecules. A dumbbell-shaped area of electron density is created by the overlapping orbitals above and below the internuclear axis. P-orbital or hybridized orbital contact forms pi bonds, which are always parallel to the internuclear axis. They can be found in compounds like ethylene (C2H4), which has one sigma bond and one pi bond in its carbon-carbon double bond. Pi bonds are frequently used in double and triple bonds between atoms and are usually weaker than sigma bonds. Pi bonds are created by the horizontal overlap of atomic orbitals, as opposed to sigma bonds, created by the head-on overlap of atomic orbitals. Pi bonds are created when two parallel atomic orbitals cross and exchange electrons between the atoms. The stability and structure of molecules depend on sigma bonds, a basic component of covalent bonding. Hybrid orbitals explain the chemical geometry and bonding in methane, ethylene, and acetylene molecules. In the hybridization process, in which atomic orbitals combine to create hybrid orbitals with various shapes and orientations, sigma bonds also play a significant part. The overlap of the atomic orbitals affects the strength of a sigma bond, with more overlap producing a stronger bond. They can be found in all different molecules, including complex organic compounds and diatomic molecules like H2.īetween two s-orbitals, two p-orbitals, or an s and a p-orbital, sigma bonds can develop. The atoms are held together in a stable configuration by sigma bonds, usually the strongest covalent bonds in a molecule.

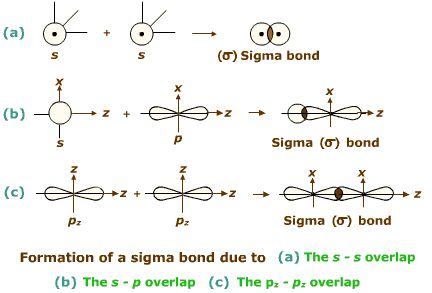
The electron density is concentrated along the internuclear axis, creating a cylindrical shape that resembles the Greek letter sigma, which is why the bond is known as a sigma bond. When two atomic orbitals cross over directly to exchange electrons between atoms, sigma bonds are created. Predicting these molecules' chemical and physical characteristics requires understanding of covalent bonding. Single bonds share one pair of electrons, double bonds share two pairs of electrons, and triple bonds share three.Ĭovalent bonds must be formed for organic and other complex molecules found in nature to survive. Three types of bonds share single, double, and triple electrons. A polar covalent bond is created when two atoms with different electronegativities share their electrons inequitably.Ĭovalent bonds can also be categorized as single, double, or triple, depending on how many electron pairs are exchanged between the atoms. A nonpolar covalent bond is created when two atoms exchange electrons equally and have comparable electronegativities. An atom's capacity to draw electrons to itself is known as electronegativity. The number of shared electrons and the atom's electronegativity determine how strong a covalent connection is. Atoms share one or more pairs of electrons in covalent bonds to attain a stable electron configuration. This kind of bonding usually takes place between atoms of non-metals. The Fundamentals of Covalent BondingĪtoms share electrons to create a bond in a chemical bonding called covalent bonding. In organic chemistry and the study of molecule structures, it is crucial to comprehend the distinction between sigma and pi bonds. These bonds have varying strengths and properties because the atoms share electrons. Sigma () bonds and pi () bonds are two different covalent interactions. One of the most prevalent kinds of chemical bonding is covalent bonding, in which two atoms share an electron to create a bond. The electronegativity of the atoms involved and the number of electrons they can share or transfer determine the type of bond created. Atoms can share or transfer electrons with other atoms to create chemical bonds. The mechanism by which atoms combine to form molecules is known as chemical bonding. Next → ← prev Difference Between Sigma Bond and Pi Bond


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
